Description
The effective operation of large organizations, such as commercial holdings, financial and government structures, largely depends on the ability to unite distributed branches into a single virtual secure network. For these purposes, the star topology is often used, where the Hub is the router in the central office, and the Spoke is the router in the branches. The units exchange data with the headquarters through secure tunnels.
The classic site-to-site VPN implementation of this scheme has a serious drawback — static tunnels need to be manually configured for connecting nodes with the central office and among themselves, which leads to an increase in the volume of configurations, the number of configured devices, the implementation time and an increase in the number of errors. In organizations with large, extensive infrastructure, such as in the banking sector with tens of thousands of ATMs, such restrictions become critical.
The problem is solved by a more versatile and convenient method of building a virtual network — the use of Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) technology, which is supported by the ESR series service routers. In the 3rd quarter of 2025, the device range was expanded with two high-performance new products such as ESR-3250 and ESR-3350. Let's take a closer look at our solution.
For a detailed design guide on creating a virtual network based on DMVPN technology, see the Eltex Design Guides section.
Solution architecture
We use DMVPN technology to establish secure communication channels between the central office and remote branches. This approach provides a more scalable and flexible alternative to traditional site-to-site connections, reducing the amount of manual configuration and speeding up network deployment.
A key advantage of DMVPN is the ability to establish direct dynamic tunnels between two Spoke routers, providing an optimal traffic route within the network. Network scaling occurs without the need to make changes to existing routers: when adding a new node, only the node itself is configured. The technology also supports dynamic assignment of tunnel IP addresses on Spoke routers, which simplifies the management of remote points.
DMVPN is an "assembler" technology that includes:
- IPsec — technology that implements encryption of the communication channel, ensuring secure data transmission between offices;
- GRE tunneling — its use supports multicast and broadcast traffic in communication channels between branches, allowing the use of the full range of network protocols operating in corporate networks;
- NHRP – protocol underlying DMVPN technology, allowing for minimal configuration on routers at the headquarters, as well as the creation of temporary tunnels between branch offices. This reduces the load on routers at the headquarters and decreases communication delays between offices.
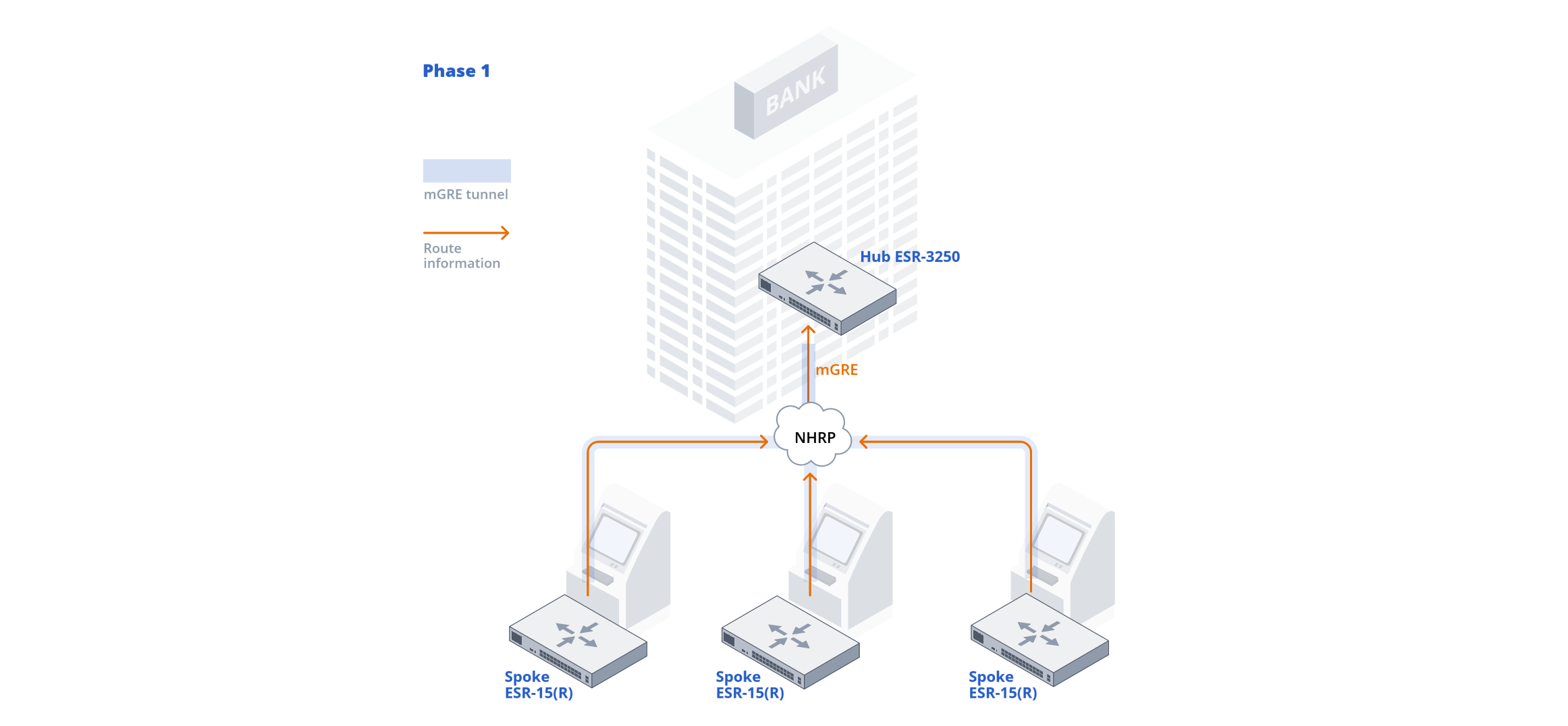
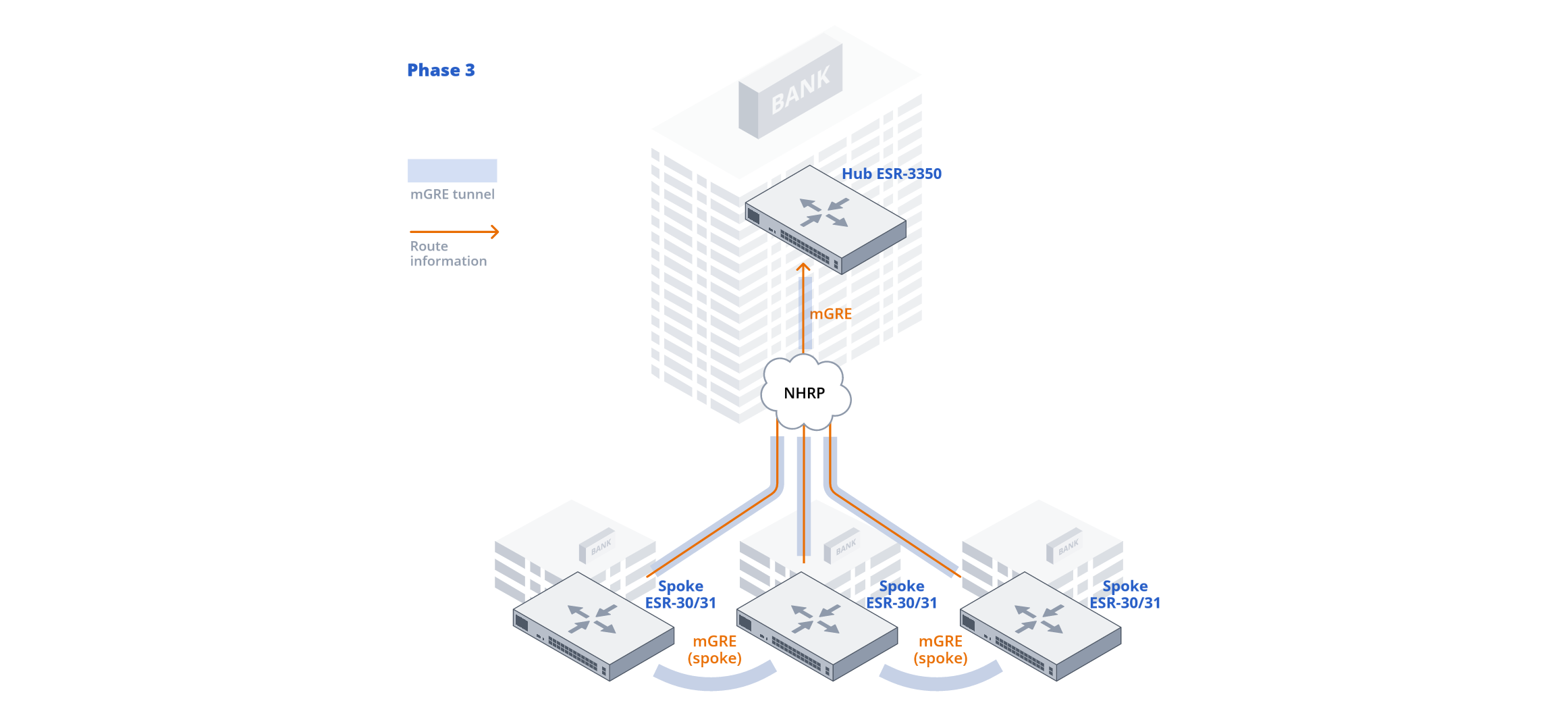
In DMVPN, there are three types of Spoke and Hub interactions, known as phases.
Support for DMVPN and three phases of operation is implemented in ESR service routers. Next, we will examine their capabilities using the example of new models used as Hubs and less powerful models as Spokes.
DMVPN-hub
Routers acting as DMVPN-Hub from the perspective of the NHRP protocol function as NHS (Next Hop Server). The routers accept registrations of new DMVPN cloud participants and allow the establishment of direct tunnels between participants (Spoke-to-Spoke) in the second and third phases. Thus, the main part of the NHRP configuration on the Hub is related to processing incoming requests from Spoke routers.
As part of an integrated solution for building a distributed network, we use ESR-3250 and ESR-3350 routers as the Hub. When encrypting traffic, they provide data transfer speeds of up to 5.3 Gbps (ESR-3250) and 14.5 Gbps (ESR-3350) in IMIX mode.
Both models are very similar to each other, but differ in performance. The ESR-3250 provides routing and traffic filtering at speeds over 50 Gbps, while the ESR-3350 – over 100 Gbps.
Routers support label-switched data (MPLS), which allows building MPLS networks over DMVPN. Additionally, the devices can fully perform firewall functions. For this purpose, a wide range of security mechanisms is implemented (IPS/IDS, AppControl in Firewall, Web Filtering, etc.)
Clustering is performed in Active/Standby mode (1+1). This ensures continuous operation of services even in the event of individual node failures.
Both classic tools (CLI, SNMP) and the ECCM management system are available for administration. The ECCM automates configuration, software updates, and equipment monitoring.
DMVPN-Spoke
The ESR-15(R), ESR-30, ESR-31 models are used as Spoke for connecting small and medium branches. The routers support DMVPN, IPsec, and MPLS, providing reliable communication with the central office.